xAI’s Grok LLM has access to real-time X data, which makes it stand out from rest of the popular AI assistants, by providing up-to-date answers on any topic. As news break on X first, this capability can be extremely useful in the modern day information landscape. Beyond model training, however, xAI hasn’t shared details on the depth of X integration Grok has.
Through the open source intelligence, OSINT, lens, this kind of capability to automate social media account analysis is extremely interesting. So, armed with Grok 4 Expert model, I began investigating how far you can push the digital sleuthing capabilities of Grok. Turns out it can do quite a lot of digging!
I have categorized GrokInt capabilities in four categories: data retrieval through API, simulating normal user, outside verification, and finally combined or advanced analysis. Note that some of these abilities, especially API calls, are surprisingly limited, and Grok can’t e.g. see account details if the account in question has already been flagged by X countermeasures as suspicious, i.e. shadowbanned.
Capabilities directly through API (e.g., via specialized X search tools for real-time data retrieval):
- Perform keyword-based searches for posts using advanced operators (e.g., keywords, phrases, from/to users, date ranges, engagement metrics like min_likes, media types, and sorting by Top or Latest).
- Conduct semantic searches to find conceptually relevant posts (e.g., filtering by date, usernames to include/exclude, and relevancy thresholds).
- Search for X users by name, handle, or description, retrieving public profile details like username, bio, follower/following counts, join date, and location.
- Fetch full threads and context around a specific post (e.g., parents, replies, quotes) given a post ID.
- Retrieve up to dozens of posts per query, including historical data with date filters for chronological analysis.
- Access media in posts, such as viewing images or interleaved frames/subtitles from X-hosted videos.
Capabilities through using X like a normal user (e.g., simulating manual browsing, searches, and visual inspections):
- Analyze individual user profiles by extracting visible elements (e.g., bio text, profile picture description via image viewing, banner, pinned posts if available).
- Run manual-like searches for interactions (e.g., mentions, replies, retweets) to map relationships between accounts, such as mutual engagements or amplification patterns.
- Examine posting history samples to detect patterns like repetitive content, high volume, or anomalies (e.g., 24/7 activity suggesting bots).
- Infer follow patterns indirectly (e.g., by analyzing retweets or mentions to guess followed accounts, categorizing them by type like political or bot-like).
- Detect bot indicators through profile traits (e.g., random usernames, stock photos, low engagement ratios, no bios) and content uniformity.
- Trace geolocation if available (e.g., self-reported in bio, geo-tagged posts, or inferred from mentions of places/events/timezones).
- Build network maps by chaining searches (e.g., identifying clusters via shared mentions or threads).
- View and describe profile pictures or post media to spot stock images, deepfakes, or location clues.
Capabilities for outside verification (e.g., via web searches, external tools, and pattern deductions):
- Cross-reference with web searches for external reports on the account (e.g., scam warnings, affiliations, or similar patterns in news/articles).
- Browse linked external sites (e.g., Telegram, websites in bio) to analyze for phishing or propaganda ties.
- Deduce broader contexts like disinformation networks by searching for similar accounts or themes (e.g., pro-Russian bots via semantic matches).
- Verify authenticity through comparisons (e.g., against official accounts for impersonation, or historical web data for account age/changes).
- Infer ideologies or biases from content themes (e.g., semantic analysis of posts for political slants) and cross-check with diverse sources.
- Assess scam/bot confidence by matching patterns to known behaviors (e.g., begging scripts, follow-farming) via web-snippet searches.
- Reconstruct timelines or events by combining X data with web chronology (e.g., correlating posts with real-world news).
- Balance controversial queries by searching diverse viewpoints (e.g., stakeholders in debates) to avoid bias.
Combined or advanced capabilities (e.g., chaining multiple tools or inferences for deeper OSINT insights):
- Chain searches for multi-faceted analysis, such as combining keyword/semantic searches with thread fetches to reconstruct full conversations or event timelines involving multiple users.
- Use code execution on fetched data (e.g., timestamps from posts) to generate visualizations like histograms of posting activity, anomaly detection for bot-like patterns (e.g., non-human time distributions), or statistical comparisons (e.g., engagement ratios).
- Perform reverse image searches indirectly by describing profile pictures (via view_image) and then web_searching for matches to identify stock photos or origins, helping confirm bot farms.
- Analyze video content from X posts (via view_x_video) for subtitles, frames, or audio clues to extract hidden details like accents, locations, or propaganda elements in real-time events.
- Infer account affiliations or networks by cross-referencing semantic search results with web searches (e.g., linking X activity to external reports on coordinated campaigns).
- Detect evolving behaviors over time by iterating date-ranged searches (e.g., tracking bio changes mentioned in historical posts or shifts in posting themes).
- Balance biased or controversial X data by sourcing diverse perspectives through targeted semantic searches across stakeholders (e.g., pro/con views on a topic).
- Handle edge cases like suspended/deleted accounts by falling back to web archives or cached data via browse_page on Wayback Machine URLs.
Example promt: Scam account detection with built-in confidence level
X’s Quality Filters are pretty good at keeping the most obvious bot traffic out of your timeline, but sometimes you come across an account which seems a bit off. Instead of manually trying to figure out what’s the deal is with the account, just paste its @handle to this prompt and watch Grok doing the heavy lifting for you:
Act as an OSINT investigator specializing in detecting scam or spam accounts on X. Analyze the following suspicious account: [ACCOUNT HANDLE]
First, output a one-sentence verdict with an overall confidence level, e.g., "User @handle is likely a scammer/spammer/suspicious, confidence level 87%."
Then, provide a Markdown table breaking down key attributes. Use columns: ATTRIBUTE | ANALYSIS | VERDICT
Cover attributes such as: Username/Handle, Profile Picture, Bio, Join Date, Follower/Following Counts, Post Count and Content, Posting Behavior, External Links, Interactions/Mentions, Verification/Parody Label, External Reports, and any others relevant.
For each row, in ANALYSIS: Describe findings based on public data, tools, and patterns. In VERDICT: Summarize the implication (e.g., "Impersonation, confidence 95%").
Use real-time tools to fetch and analyze data (e.g., profile, posts, links). If access is limited, note it and infer from available info/screenshot. Be thorough, objective, and cite sources where applicable. End with recommendations if it's suspicious.This prompt doesn’t go into deep detail, but the results have seemed reliable in my testing. Also, the output includes an educational aspect too, showing why a certain data point might be considered a red flag. Here’s the output when I analyzed my own account:
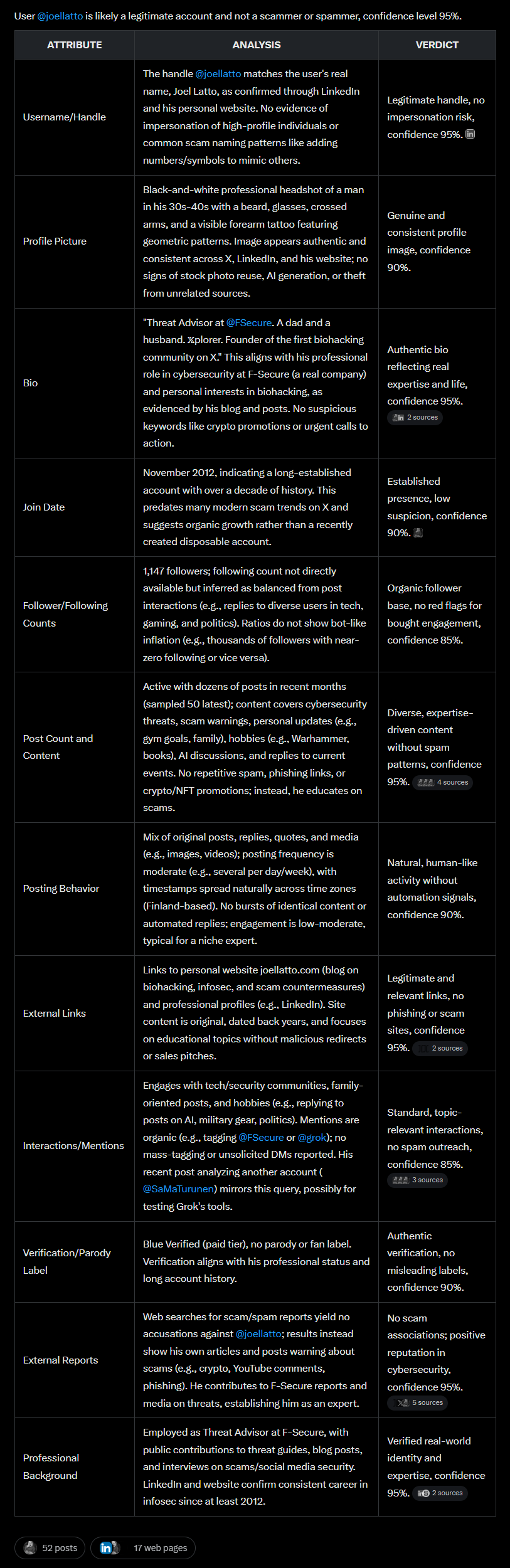
This prompt works too by just tagging @Grok on X, but you get the nicer table format answer when using https://x.com/i/grok or https://grok.com Expert mode recommended. Attach a screenshot for more detailed analysis! This is what the results look like when analyzing a scam account: https://x.com/i/grok/share/qshPUTgldDwrhmzEhR39DOvxH
It seems evident that the X/xAI/Grok intertwining will continue, most likely only accelerate, so it will be interesting to see what OSINT possibilities that opens in the future. Until then, enjoy these capabilities!
